|
|
|
|
|
|
Thus, a descriptor for languages maps each natural number into a collection of languages, and similarly for descriptors for functions. In the context of descriptor DL, we call 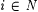 a "description" of DL(i). Description i may be conceived as an inductive inference problem posed to a scientist, namely, the problem of identifying DL(i). A well-rounded, generally intelligent scientist should respond to i by adapting her scientific strategy in such a way that she identifies the described collection DL(i). Here are two examples of descriptors that will occupy us in the sequel. a "description" of DL(i). Description i may be conceived as an inductive inference problem posed to a scientist, namely, the problem of identifying DL(i). A well-rounded, generally intelligent scientist should respond to i by adapting her scientific strategy in such a way that she identifies the described collection DL(i). Here are two examples of descriptors that will occupy us in the sequel. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) [·] denotes the descriptor for languages defined as follows. For all 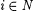 , , 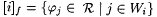 . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) [·]f denotes the descriptor for functions defined as follows. For all i 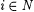 , , 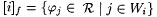 . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thus, [·] interprets i as the collection of all languages with indexes in Wi. [·]f interprets i as the collection of all total recursive functions with indexes in Wi. Note that Wi may well contain indexes j such that j j is only partial, hence not a member of 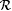 . Such partial functions j j are not described by [i]f and hence do not figure in the scientific problem posed by i. Indexes in [i]f for nontotal functions should thus be considered as "noise" in the description. No such noise occurs for [·]. In this sense, [·] is more transparent than [·]f. . Such partial functions j j are not described by [i]f and hence do not figure in the scientific problem posed by i. Indexes in [i]f for nontotal functions should thus be considered as "noise" in the description. No such noise occurs for [·]. In this sense, [·] is more transparent than [·]f. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Given 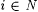 , Wi may contain equivalent indexes, that is, multiple indexes for the same language. It is thus possible for Wi to have more members than [i]. The same is true of [·]f. This is a sense in which neither descriptor is perfectly transparent. , Wi may contain equivalent indexes, that is, multiple indexes for the same language. It is thus possible for Wi to have more members than [i]. The same is true of [·]f. This is a sense in which neither descriptor is perfectly transparent. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scientists that accept descriptions of problems have an additional, numerical argument. They are thus called "parameterized." |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) A parameterized scientist for languages is any computable mapping (partial or total) from N × SEQ into N. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) A parameterized scientist for functions is any computable mapping (partial or total) from N × SEQ into N. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By "parameterized scientist" is meant either parameterized scientist for languages or for functions; context determines which kind is at issue. As a variable for parameterized scientists, we use G . |
|
|
|
|