|
|
|
|
|
|
if A is infinite and 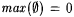 . By convention, min(x1, . . ., xk) = min({x1, . . ., xk}) and max(x1, . . . ,xk) = max({ x1, . . ., xk}). For each . By convention, min(x1, . . ., xk) = min({x1, . . ., xk}) and max(x1, . . . ,xk) = max({ x1, . . ., xk}). For each 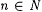 , A[n] denotes , A[n] denotes 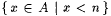 . A - B denotes the set . A - B denotes the set 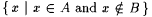 . For . For 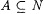 , , 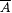 denotes the complement of A, that is, N - A. A D B denotes the symmetric difference of A and B, that is, denotes the complement of A, that is, N - A. A D B denotes the symmetric difference of A and B, that is, 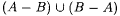 . . 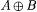 denotes the disjoint union of A and B, that is, denotes the disjoint union of A and B, that is, 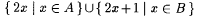 . For each . For each 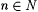 , A = n B means that , A = n B means that 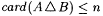 ; A and B are called n-variants. A =* B means that card(A D B) is finite; A and B are called finite variants. ; A and B are called n-variants. A =* B means that card(A D B) is finite; A and B are called finite variants. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For each finite set A, we define the canonical index of A to be the natural number 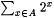 . (The canonical index of . (The canonical index of 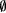 is thus 0.) The canonical indexing provides a one-to-one correspondence between finite sets and the natural numbers. Dx denotes the finite set whose canonical index is x(see Rogers [l58]) is thus 0.) The canonical indexing provides a one-to-one correspondence between finite sets and the natural numbers. Dx denotes the finite set whose canonical index is x(see Rogers [l58]) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For natural numbers x and z, let: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Let R denote the set of real numbers. For each a and 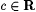 , let: , let: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As usual, '' and $ are used for universal and existential quantifiers. 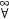 , , 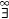 , and $ ! denote 'for all but finitely many,' 'there exist infinitely many,' and 'there exists a unique.' That is: , and $ ! denote 'for all but finitely many,' 'there exist infinitely many,' and 'there exists a unique.' That is: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
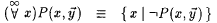 is finite. is finite. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
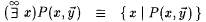 is infinite. is infinite. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
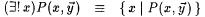 is a singleton. is a singleton. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The symbols  , , 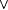 , and , and 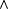 , respectively, denote logical negation, or and and. Fix an , respectively, denote logical negation, or and and. Fix an 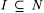 , and, for each , and, for each 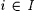 , let , let 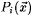 be a predicate. Then, be a predicate. Then, 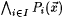 denotes denotes 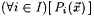 and and 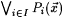 denotes denotes 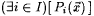 . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Let A and B be arbitrary sets (that is, not necessarily subsets of N). Then 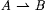 (respectively, (respectively, 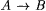 ) denotes the collection of all partial (respectively, total) functions from A to B. Unless otherwise specified, when we say y is a partial function we will mean that y : ) denotes the collection of all partial (respectively, total) functions from A to B. Unless otherwise specified, when we say y is a partial function we will mean that y : 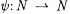 and when we say f is a total function, we will mean and when we say f is a total function, we will mean |
|
|
|
|